What Is Product Data Management (PDM)?
Blog Article | November 24, 2025
Author: Sassan Khoubyari
Director, PLM & Digital Transformation
- Over 20 years of technical implementation, strategy development and management experience in PLM, IT for global product development operations(Auto and Aerospace)
- Expertise in PLM, IT technology evaluation, selection, configuration and implementation with structured project management practices
- Proven track record of process improvement implementation, executive reviews and overall system support
- Managed technical staff and vendors in successful multi million dollars technology and process implementation
Summary & Key Topics
Product Data Management (PDM) organizes, secures, and shares engineering and product development data. It provides a single source of truth, ensuring version control, traceability, and cross-functional collaboration. Modern PDM integrates with CAD, PLM, and enterprise systems to streamline workflows, reduce errors, and support compliance—enabling faster, more efficient, and innovation-ready product development.
Key Topics Covered:
-
PDM definition and importance
-
Risks of unmanaged data: lost IP, outdated versions, compliance gaps
-
PDM capabilities: vaulting, metadata, version control, CAD integration, visualization, mobile access
-
Applications: design, manufacturing, quality, procurement, service
-
Adoption challenges: data silos, manual workflows, inconsistent documentation
-
Tools & technologies: Teamcenter, Aras, Windchill, NX Data Management, cloud, visualization tools
-
Best practices: governance, validation, collaboration, security, backups
-
Future trends: AI automation, AR/VR, IoT, cloud/hybrid, responsible data use
-
PDM vs PLM: data/files vs full product lifecycle management
-
Strategic value: collaboration, error reduction, compliance, efficiency

Product Data Management (PDM)
In the world of modern engineering, data is the foundation of innovation. From CAD models and simulations to compliance documents and change orders, the volume and complexity of engineering data has grown exponentially. Without a robust strategy to organize, manage, and secure this information, teams risk delays, errors, and missed opportunities.
Product Data Management (PDM) is the discipline and systematized process of collecting, storing, organizing, sharing, and securing all the data associated with product development and engineering activities. For manufacturers, design teams, and product developers, PDM plays a critical role in ensuring projects are delivered faster, with fewer errors, and with greater visibility across teams and systems.
Why Product Data Management Is Important
Engineering data is unlike standard business data. It includes intricate CAD files, large simulation datasets, version-controlled documents, specifications, bills of materials, and more. Managing this data requires not only storage, but structure, context, traceability, and security.
Without Proper PDM:
- Engineers waste time searching for files.
- Teams work on outdated versions.
- Intellectual property is vulnerable to loss or misuse.
- Compliance and audit trails become difficult to maintain.
A robust PDM strategy ensures design integrity, cross-functional collaboration, and traceability throughout the product lifecycle. It’s foundational to innovation, regulatory compliance, and digital transformation.

Key Capabilities & Benefits of PDM Systems
Modern PDM solutions go beyond basic storage. They deliver powerful features that enhance productivity, collaboration, and quality:
Centralized Document Vaulting
All engineering assets are stored in one secure, searchable repository—accessible to authorized users across teams and locations.
Smart Metadata Use & File Naming
Automated metadata tagging (e.g., part number, project ID, revision) helps with indexing and retrieval. Intelligent file naming reduces confusion and supports automation.
Automated Version Control & Transmittals
PDM solutions automatically track document revisions, notify users of updates, and generate transmittals for suppliers and partners, ensuring everyone works from the latest information.
CAD Integration & File Relationship Management
PDM connects directly to leading CAD systems (NX, Solid Edge, etc.), preserving file dependencies and preventing broken references or overwritten geometry.
Integrated Visualization & Markup
Non-CAD users can view, redline, and comment on engineering documents directly within the PDM platform, eliminating the need for extra software or file conversions.
Mobile Access & Platform Interoperability
Access and update files on the go via mobile apps or web clients. Interoperability with PLM and ERP systems streamlines workflows and enhances data consistency across the enterprise.
PDM in Practice: Applications Across Engineering Functions
Design Engineering
Manage CAD models, assemblies, design changes, and release workflows.
Manufacturing Engineering
Access up-to-date production drawings, specs, and work instructions.
Quality & Compliance
Store audit trails, certifications, and non-conformance reports with full traceability.
Procurement & Supply Chain
Collaborate with suppliers using controlled document access and transmittals.
Service & Support
Reference product documentation and historical revisions for maintenance and field service activities.
Common Challenges in Product Data Management
Despite its many advantages, companies often struggle to implement Product Data Management effectively. One of the most common issues is the lack of a centralized source of truth—files are scattered across shared drives, emails, and individual desktops, making it difficult to locate the latest version or maintain a complete project record. Manual workflows such as spreadsheets, email chains, and paper-based processes also lead to inefficiencies, delays, and a higher risk of miscommunication. In organizations with multiple teams or locations, disconnected systems create data silos, resulting in duplicate work, inconsistent documentation, and limited collaboration. Without proper version tracking, approval workflows, or metadata tagging, maintaining traceability and meeting compliance requirements becomes increasingly difficult—especially when historical records or audit trails are needed.
Ready to Simplify Your Data Management?
Contact Saratech for a consultation or demo of our PDM and PLM solutions.
Tools & Technologies in PDM
The PDM ecosystem includes a range of technologies that support data management:
- PLM Platforms (e.g., Siemens Teamcenter, Aras, Windchill)
- Document Management Systems (e.g., Adept, M-Files)
- CAD Data Management Tools (e.g., NX Data Management, Solid Edge SP)
- Cloud Storage Solutions with Engineering Add-ons (e.g., Autodesk Vault, SharePoint + custom integrations)
- Enterprise Search Engines for engineering files
- Visualization and Markup Tools (e.g., JT2Go, PDF redlining)
Many organizations adopt a combination of these tools to match their scale, industry, and IT landscape.
Best Practices for Effective Product Data Management
To get the most out of PDM, follow these guiding principles:
Establish a Robust Data Governance Framework
Define data ownership, naming conventions, access rights, and change control policies.
Ensure Data Quality, Validation, & Standardization
Clean, standardized data is the foundation of automation, analytics, and traceability.
Enable Cross-Functional Collaboration
Involve design, manufacturing, procurement, and quality teams in PDM strategy and tool selection.
Implement Strong Security & Access Controls
Protect sensitive IP with role-based access, encryption, and secure sharing protocols.
Plan for Regular Backups & Disaster Recovery
Ensure business continuity with automated backups, redundancy, and tested recovery plans.
Future Trends in Product Data Management
As engineering complexity continues to rise, PDM systems are evolving to meet new demands. We can expect the growing integration of AI-powered automation, offering intelligent file categorization, predictive issue detection, and smarter search capabilities. Augmented and virtual reality (AR/VR) will increasingly support immersive design reviews and layout planning, bringing greater visualization into the engineering process. Meanwhile, IoT integration will allow sensor data to flow directly into PDM systems, supporting real-time design adjustments and maintenance planning. The shift toward cloud-native and hybrid architectures will help balance the need for scalability, security, and remote accessibility. Lastly, as data volume and automation increase, there will be a heightened emphasis on data ethics, transparency, and sovereignty, ensuring responsible AI use and compliance with global data governance standards.
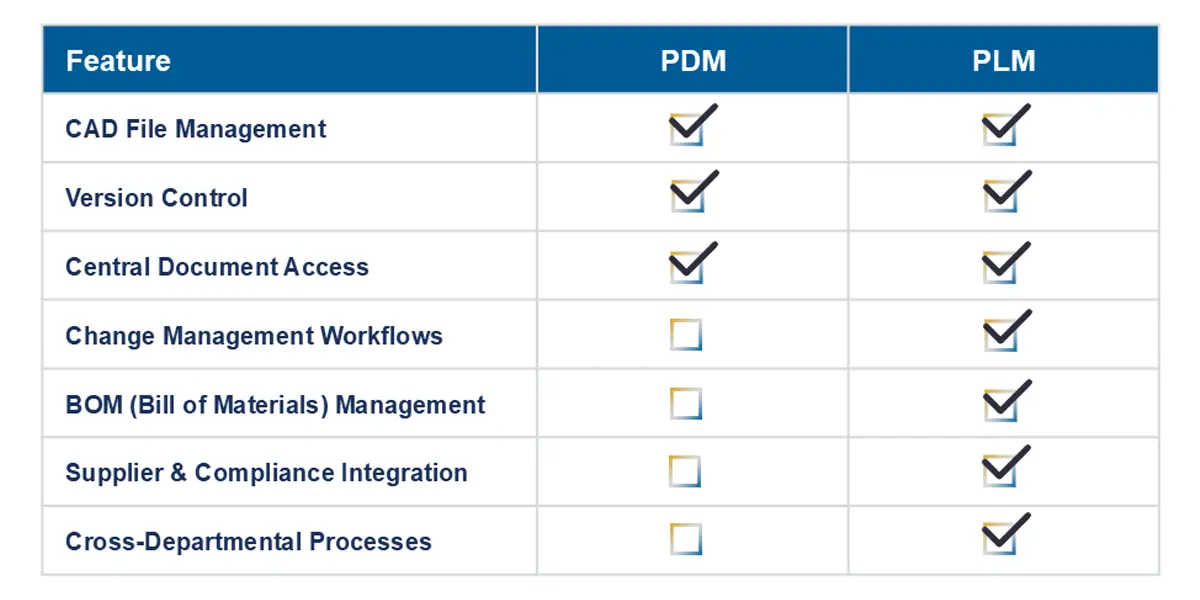
PDM vs PLM: What’s the Difference?
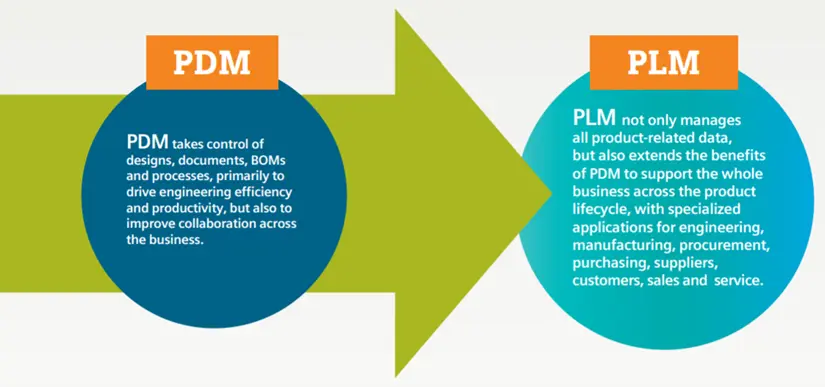
PDM
PDM focuses mostly on managing files and CAD data.
PLM
PLM (Product Lifecycle Management) manages not just the data, but the entire product development process—from requirements and configurations to BOM management, change workflows, supplier collaboration, and beyond.
Think of PDM as the foundation, a critical first step. Once your team is comfortable managing engineering files and revisions, you’re in a great position to scale up to PLM and optimize your entire product development lifecycle.
Conclusion: Why PDM Matters More Than Ever
Product Data Management is no longer optional—it’s a strategic necessity for modern product development. Whether you're building airplanes, electronics, or complex machinery, your ability to innovate hinges on how effectively you manage your engineering data.
By adopting modern PDM tools and best practices, teams can streamline collaboration, reduce errors, meet compliance goals, and unlock new levels of efficiency.
If you're still relying on shared drives, email threads, or manual folders for your engineering data—now’s the time to explore PDM. Saratech can help you:
-
Evaluate your current engineering data workflows
-
Select and implement the right PDM system for your needs
-
Plan for a future transition to PLM when the time is right


